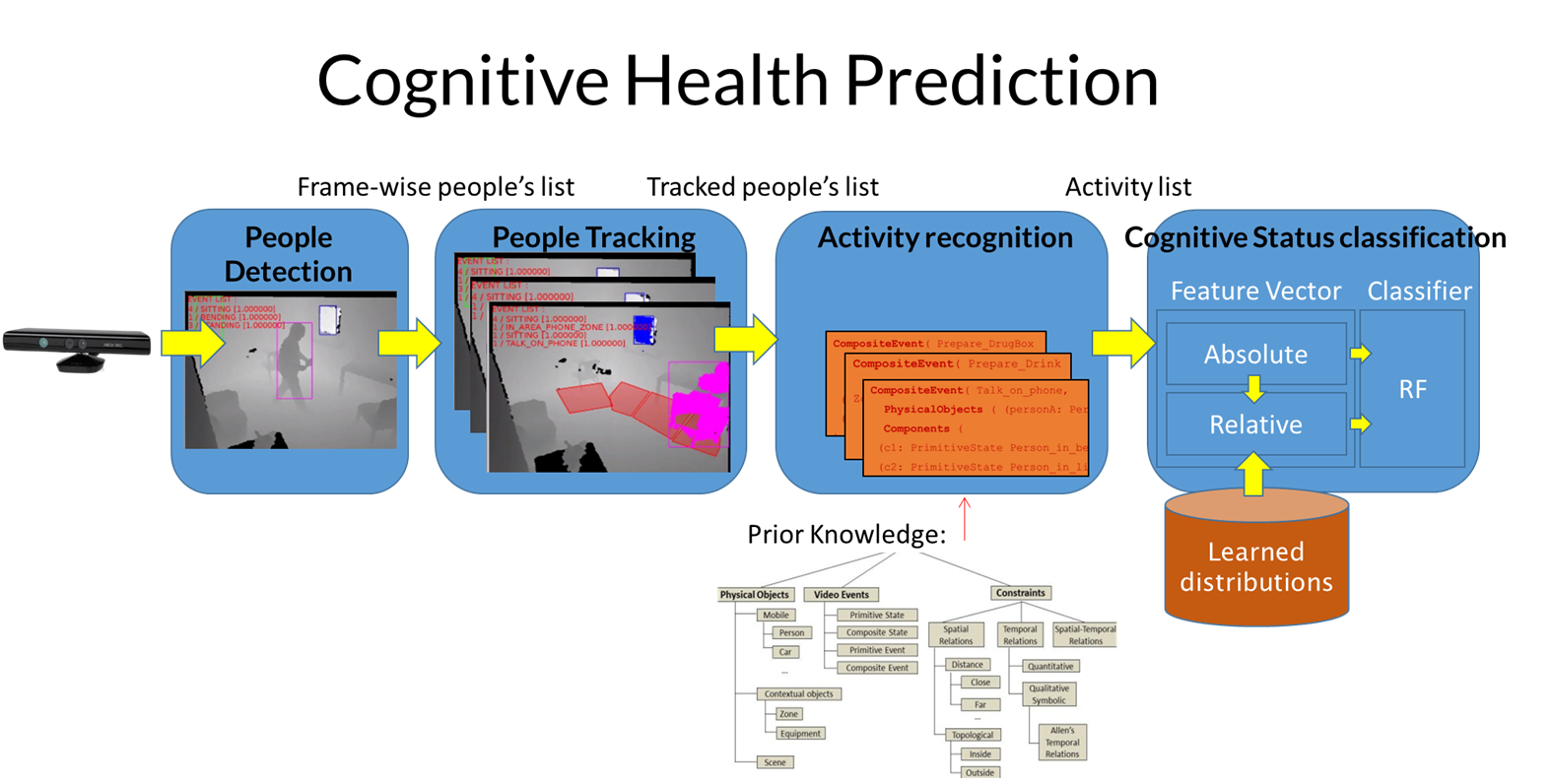
Section: New Results
On the Study of the Visual Behavioral Roots of Alzheimer's disease
Participants : Carlos F. Crispim-Junior, François Brémond.
Keywords: Activities of Daily Living, Dementia prediction, RGBD sensors, Activity Recognition, Cognitive Health
Existing computer vision studies for the diagnosis of Dementia have focused on extracting discriminative patterns between healthy and people with dementia from neuroimagery exams, like functional MRI and PET scans. Nonetheless, the effects of dementia over human behaviors are a discriminative component that is barely explored by automatic vision-based methods. We studied a framework to automatically recognize the cognitive health of seniors from the visual observation of their activities of daily living (Fig.16). We employ a lightweight activity recognition system based on RGBD sensors to recognize the set of target activities (e.g., prepare drink, prepare medication, make a payment transaction) performed by a person in a continuous video stream. Then, we summarize the absolute and relative activity patterns present in the video sequence using a novel probabilistic representation of activity patterns. Finally, this representation serves as input to Random Forest classifiers to predict the class of cognitive health that the person in question belongs to. We demonstrate that with the current framework can recognized the cognitive health status of seniors (e.g., healthy, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's disease) with an average F-score of 69 % in real life scenarios.
|